“A picture is worth a thousand words, and all of these photos showcase projects completed by our company, demonstrating our proven capability and responsibility over our 23 years of experience in delivering the best to our clients.”
Commercial and Industrial Steel or Wood Building
We have professional and technical staff, as well as the equipment and materials to construct any industrial or commercial building with either steel or wood framing. We start from creating the 3D design of the building in collaboration with the client to tailor it to their needs, and we continue through to the final finishes, always striving to optimize costs and performance for our clients.
Industrial Building
Industrial building construction refers to the process of planning, designing, and building structures intended for industrial or manufacturing purposes. These buildings are specifically engineered to accommodate various industrial operations, machinery, and production processes. Here are some key aspects of industrial building construction:
- Planning and Design: The process begins with thorough planning and design. Industrial structures need to be designed to meet the specific needs of the industry they serve, whether it’s manufacturing, warehousing, research and development, or any other industrial activity. This involves considering factors like floor layout, ceiling height, utility systems, and compliance with safety and environmental regulations.
- Site Selection: Selecting an appropriate location is crucial. Factors such as proximity to suppliers, customers, transportation routes, and the availability of utilities and infrastructure play a significant role in the site selection process.
- Building Materials: The choice of construction materials depends on the nature of the industrial activities. Common materials include steel, concrete, and pre-engineered building components. These materials provide strength, durability, and flexibility in design.
- Utility Systems: Industrial buildings require robust utility systems, including electrical, plumbing, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), and sometimes specialized systems like compressed air or wastewater treatment. These systems need to be designed and installed to support the industrial processes efficiently and safely.
- Safety and Compliance: Industrial buildings must adhere to strict safety and environmental regulations. Compliance with codes and standards is essential to ensure the safety of workers and the surrounding community, as well as to minimize the environmental impact.
- Zoning and Permits: Obtaining the necessary permits and adhering to zoning regulations is a critical part of the construction process. Local authorities typically have guidelines and requirements that must be met.
- Equipment and Machinery Installation: After the building’s shell is complete, the installation of industrial equipment and machinery takes place. This may require specialized knowledge and coordination to ensure that the machinery functions optimally within the facility.
- Customization: Industrial buildings can be customized to meet specific operational needs, including office spaces, storage areas, loading docks, and more.
- Maintenance and Upkeep: Once the building is operational, ongoing maintenance and upkeep are essential to ensure its long-term functionality and safety.
- Expansion and Adaptation: Industrial structures often need to be adaptable to changing requirements. They may need to accommodate expansions, changes in production processes, or new technologies.
Industrial building construction is a complex and highly specialized field that requires collaboration among architects, engineers, construction professionals, and industry experts to create safe, efficient, and cost-effective structures for industrial purposes.
[smartslider3 slider=”3″]
Residential Barndominiums Projects


A “barndominium” is a portmanteau of “barn” and “condominium,” and it refers to a type of building that combines both residential living space and areas traditionally associated with a barn or other storage or workspace. Barndominiums have gained popularity in recent years, especially in rural and agricultural areas. They are often constructed using the outer shell or framework of a barn or similar structure and then converted into a living space, while retaining some elements of the original structure.
Typically, a barndominium may feature a large open space for a living area, kitchen, and dining room, and then have separate areas for bedrooms, bathrooms, and potentially a workspace or storage. They can be designed to have a rustic or industrial look, and they are often praised for their spacious and open floor plans.
Barndominiums are known for their versatility and can be used as primary residences, vacation homes, or even event venues. They offer a unique and customizable approach to housing that appeals to those looking for a combination of rural charm and modern amenities.
Interior Finish First Quality
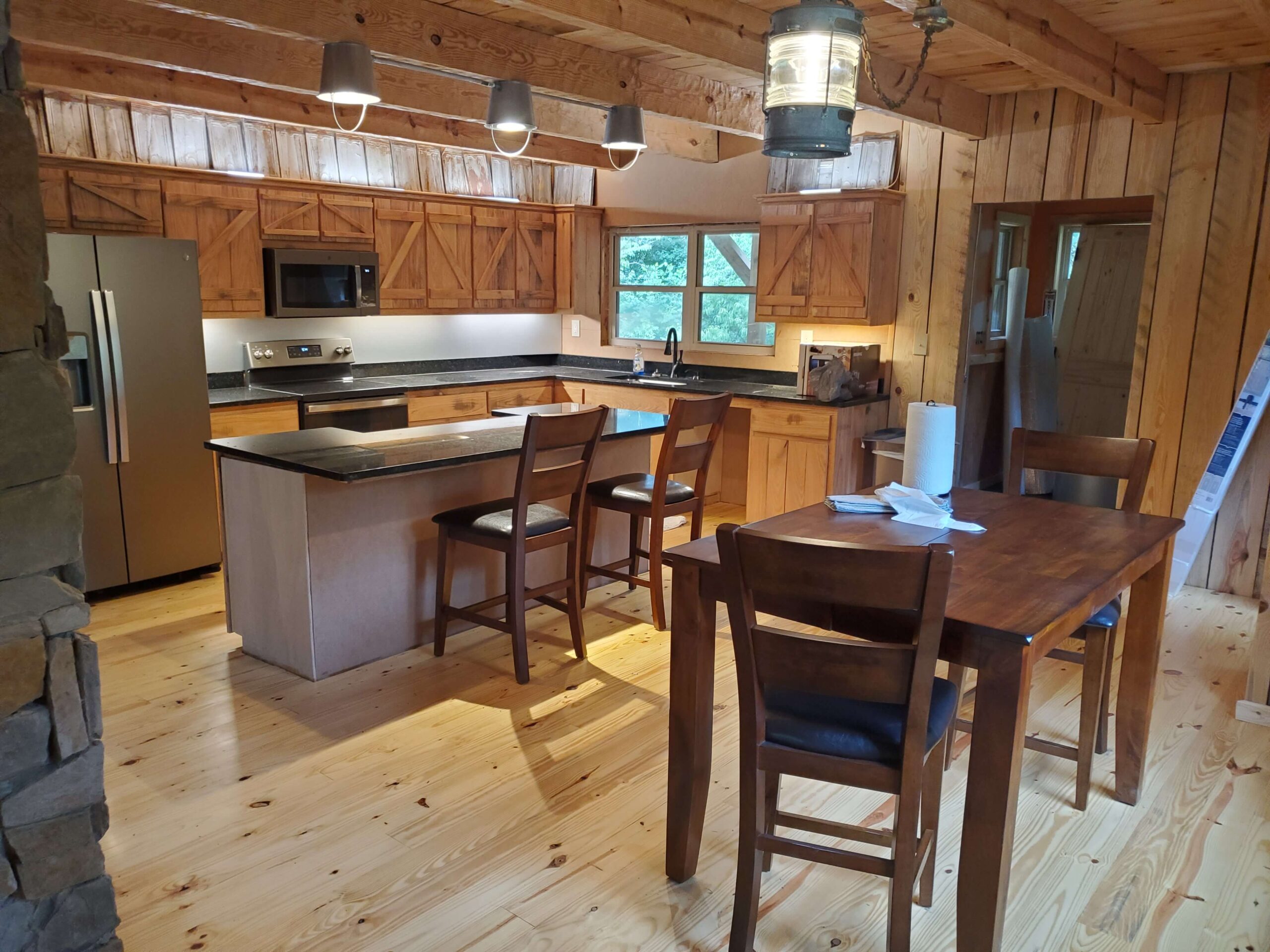
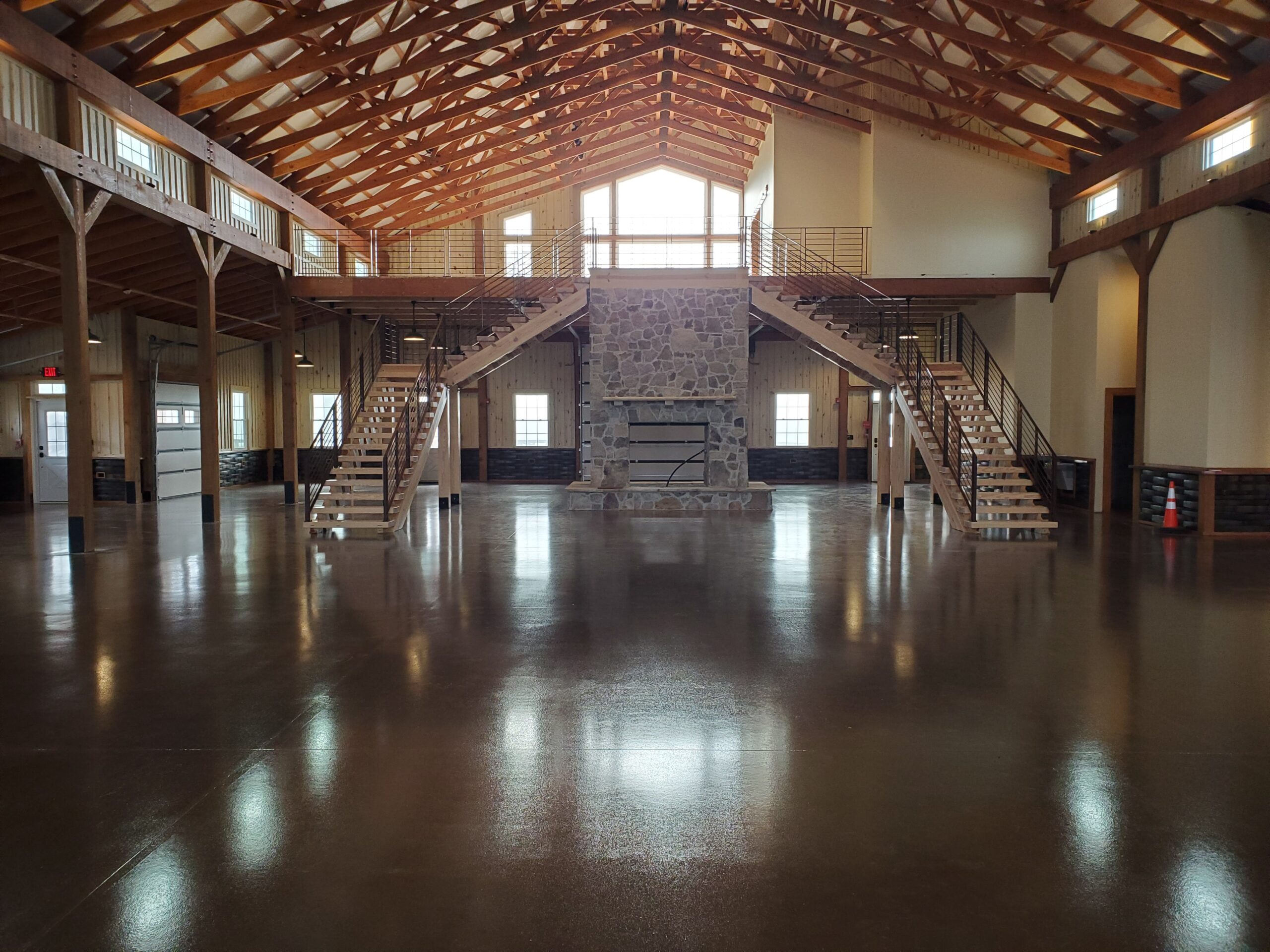


“Interior finish first quality” generally refers to a high standard of materials and craftsmanship used in the interior finishing of a building. When an interior finish is described as “first quality,” it typically means that premium materials and skilled workmanship have been employed to create a superior, well-crafted, and visually appealing interior. Here are some aspects associated with “interior finish first quality”:
- High-Grade Materials: First-quality interior finishes use top-grade materials that are not only durable but also aesthetically pleasing. This might include premium wood, stone, metal, or other materials, depending on the design and purpose.
- Attention to Detail: Attention to detail is a hallmark of first-quality interior finishes. The craftsmanship is precise, and the finishing touches are meticulously executed.
- Fine Workmanship: Skilled and experienced artisans or tradespeople often handle the installation or application of interior finishes. They have the expertise to create a polished and flawless result.
- Customization: First-quality interior finishes can often be customized to meet the specific needs and preferences of the client. This may include custom millwork, unique design features, or tailored finishes.
- Durability: High-quality interior finishes are built to last. They are designed to withstand wear and tear, making them a long-term investment.
- Aesthetics: First-quality interior finishes pay great attention to aesthetics. The finishes are not only functional but also enhance the visual appeal of the space. They may include elements like decorative moldings, ornate fixtures, or artistic details.
- Functionality: While aesthetics are important, functionality is not overlooked. First-quality interior finishes should serve their intended purpose effectively. For example, they should provide proper insulation, acoustics, and functionality.
- Compliance: When applicable, first-quality interior finishes should adhere to safety, environmental, and regulatory standards. This ensures that the finished interior is not only beautiful but also safe and compliant with relevant codes.
- Quality Assurance: Quality control measures may be in place to ensure that each aspect of the interior finish meets the desired level of quality. This can include inspections, testing, and quality assurance protocols.
- Client Satisfaction: The ultimate goal of first-quality interior finishes is client satisfaction. The finished interior should meet or exceed the client’s expectations in terms of aesthetics, functionality, and durability.
First-quality interior finishes are often associated with luxury or high-end projects, but they can also be found in various settings, including residential homes, commercial spaces, and institutional buildings where the emphasis is on creating a superior and lasting interior environment.
Client-Centric Design
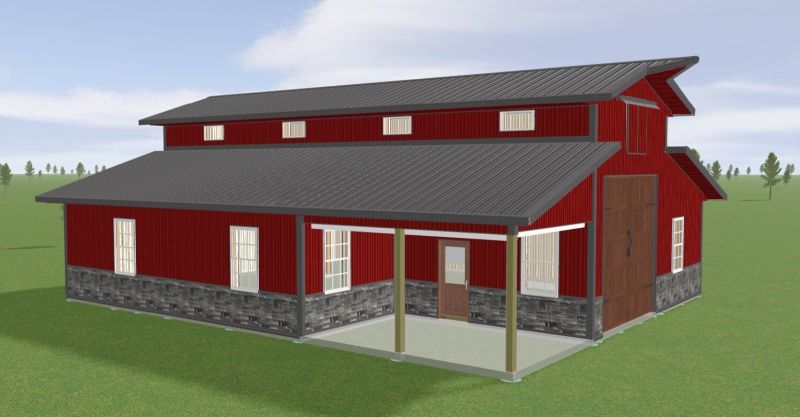
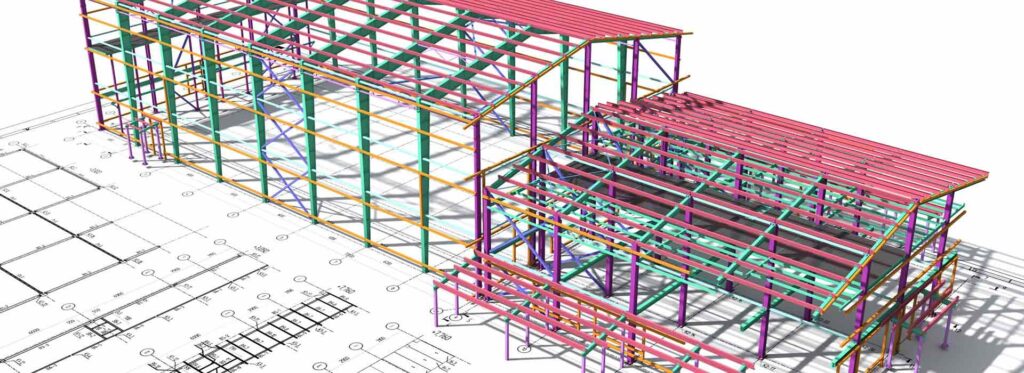

Client-centric design in 3D refers to a design approach that prioritizes the needs, preferences, and input of the client or customer in the creation of three-dimensional (3D) models or designs. This approach is often used in various industries, including architecture, interior design, product design, and more. Here are some key aspects of client-centric design in 3D:
- Client Involvement: The primary focus is on actively involving the client throughout the design process. This includes conducting initial consultations to understand their vision, goals, and requirements. The client’s feedback and ideas are continuously integrated into the 3D design.
- Collaboration: A collaborative relationship is established between the designer and the client. Regular meetings, discussions, and reviews are conducted to ensure that the 3D design aligns with the client’s expectations.
- Customization: The 3D design is customized to the specific needs and preferences of the client. This may involve tailoring architectural features, interior layouts, product aesthetics, or other design elements to match the client’s unique requirements.
- Visualization: 3D modeling and visualization tools are used to provide the client with a clear and realistic representation of the design concept. This helps clients better understand how the final product will look and function.
- Feedback Integration: Client feedback and revisions are actively incorporated into the 3D design. Design iterations are common to ensure that the final product aligns with the client’s vision.
- Functionality and Usability: The design not only focuses on aesthetics but also on the functionality and usability of the end product. It should meet the client’s practical needs and objectives.
- Cost and Efficiency: While aiming to meet the client’s vision, cost-effectiveness and efficiency are also considered. The design should be realistic in terms of budget and resources.
- Timeline Management: Client-centric 3D design also takes into account project timelines and deadlines. The design should be developed within the client’s required time frame.
- Adaptability: The design should be adaptable to changes or evolving client requirements as the project progresses.
- Client Satisfaction: Ultimately, the success of client-centric design in 3D is measured by the satisfaction of the client. If the final design aligns with the client’s expectations and requirements, it is considered a successful project.
This approach can be particularly valuable in industries where visualizing the final product is critical, as 3D design allows for a realistic preview of the end result. It ensures that the design is not just a reflection of the designer’s vision but a solution that truly serves the client’s needs and objectives.



